Supreme Court of India
*** इस पृष्ठ को हिंदी में पढ़े ***
Supreme Court of India
Important Points

- The Supreme Court of India came into existence on 28 January 1950.
- The Supreme Court moved to the present building in 1958.
- The foundation stone of the building was laid by Dr. Rajendra Prasad on 29.11.1954.
- The chief architect of the building of the Supreme Court was Ganesh Bhikaji Deolalikar, the first Indian to head the Central Public Works Department.
- The motto of the Supreme Court as inscribed on its seal is Yato Dharmastato Jayah (Whence Justice, Thence Victory)
- The Supreme Court replaced the Federal Court of India and the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council.
Chief Justice of India
Important Points
- The Supreme Court has 34 Judges including the Chief Justice of India.
- At the time of its formation in 1950, the Supreme Court had 8 judges including the CJI.
- The first Chief Justice of India was Justice Hiralal J Kania.
- The longest serving Chief Justice of India has been Justice Y.V. Chandrachud who was the CJI from 22.02.1978 to 02.07.1985 (7 years 139 days)
- The Chief Justice with the shortest tenure has been Justice Kamal Narain Singh, who was the CJI for only 17 days in December 1991.
- The Chief Justice of India administers the oath of office to the President of India.
- The Judges of Supreme Court are appointed by the President on the recommendations of the National Judicial Appointments Commission as constituted under Article 124(A) of Indian Constitution.
- The upper age limit for appointment as Supreme Court judge is 65 years.
- The Judge of Supreme Court of India is sworn in by the President or some person appointed in that behalf by him.
- The judge of Supreme Court of India may resign by wrting under his hand to the President.
Conditions for being appointed as a Judge of Supreme Court of India
Article 124(3)(a)(b)(c) deals with the conditions for being appointed as a Judge of the Supreme Court of India. The provisions are listed below in simple words:
- He must be a citizen of India.
- He must have been a Judge of a High Court or of two or more such Courts in succession for at least FIVE years.
- He must have been an advocate of a High Court or of two or more such Courts in succession for at least TEN years.
- He is, in the opinion of the President, a distinguished jurist.
Conditions for removal Judge of Supreme Court of India
Article 124(4) deals with the conditions for removal of a Judge of Supreme Court of India. The provisions are listed below in simple words:
- A Judge of Supreme Court can only be removed on the grounds of proved misbehaviour or incapacity.
- The order for removal should be passed by the President.
- Before the order by the President each house of the Parliament should present to the President an address for his removal in the same session.
- The address for his removal must have been supported by a majority of not less than two-thirds of the members of that house present and voting.

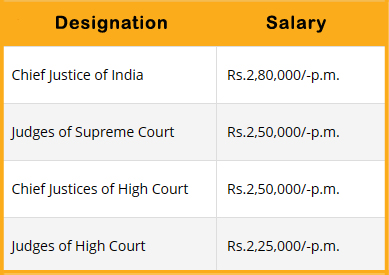
Salary of Chief Justices and Judges wef 01.01.2016