Types of Diseases
*** इस पृष्ठ को हिंदी में पढ़े ***
The study of diseases is called Pathology.
What is a disease?: A disease is a medical condition or disorder that negatively affects the structure or function of an organism. It leads to impaired physiological processes and often has characteristic symptoms.
Causes of Diseases: Diseases can arise due to various factors, including pathogens (e.g., viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites), genetic mutations, environmental factors, lifestyle choices, or a combination of these factors.
| Type of Disease | Examples |
|---|---|
| Congenital diseases | Hare lip, club foot, mongolism, spastic paraplegia |
| Hereditary diseases | Haemophilia, albinism |
| Dietary deficiency diseases | Scurvy, rickets, beri-beri, anaemia |
| Hormonal diseases | Goitre, diabetes mellitus, acromegaly, dwarfism |
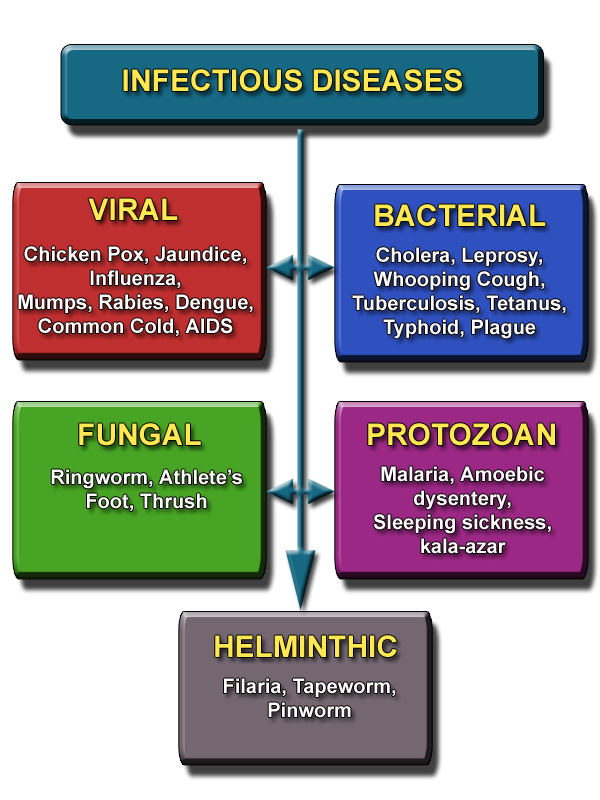
| Infectious diseases (VIRAL) | AIDS, chicken pox, common cold, german measles, influenza, jaundice, measles, mumps, poliomyelitis, rabies, dengue fever, lassa fever |
| Infectious diseases (BACTERIAL) | cholera, whooping cough, diptheria, gonorrhoea, leprosy, pneumonia, syphilis, tetanus, typhoid, tuberculosis, plague |
| Infectious diseases (FUNGAL) | ringworm, atheletes’ foot, thrush |
| Infectious diseases (PROTOZOAN) | malaria, amoebic dysentery, sleeping sickness, kala-azar |
| Infectious diseases (WORMS) | filaria, tapeworm, pinworm |
| Degenerative diseases | graying of hair, baldness, presbyopia, cataract, osteoarthritis, Parkinson’s disease, arteriosclerosis |
| Immunological diseases | hay fever, asthma, rheumatoid, arthritis, nettle rash |
| Neoplastic diseases | warts, moles, cancer |
www.leadthecompetition.in
Select the right answer
1. Which of the following is a bacterial disease?
2. What kind of disease is osteoarthritis?
3. Which of the following is a hereditary disease?
4. Which of the following is a viral disease?
5. The causative agent of malaria is a -
6. Which of the following is NOT an infectious disease?
7. Which of the following is a fungal disease?
8. What kind of disease is arthritis?
MEMORY TEST
Five of the following are infectious diseases.
Click on all possible answers