Statewise - MPs, MLAs and MLCs
*** इस पृष्ठ को हिंदी में पढ़े ***
The following is the State-wise list of Lok Sabha MPs, Rajya Sabha MPs, Members of Legislative Assembly and Members of Legislative Council.
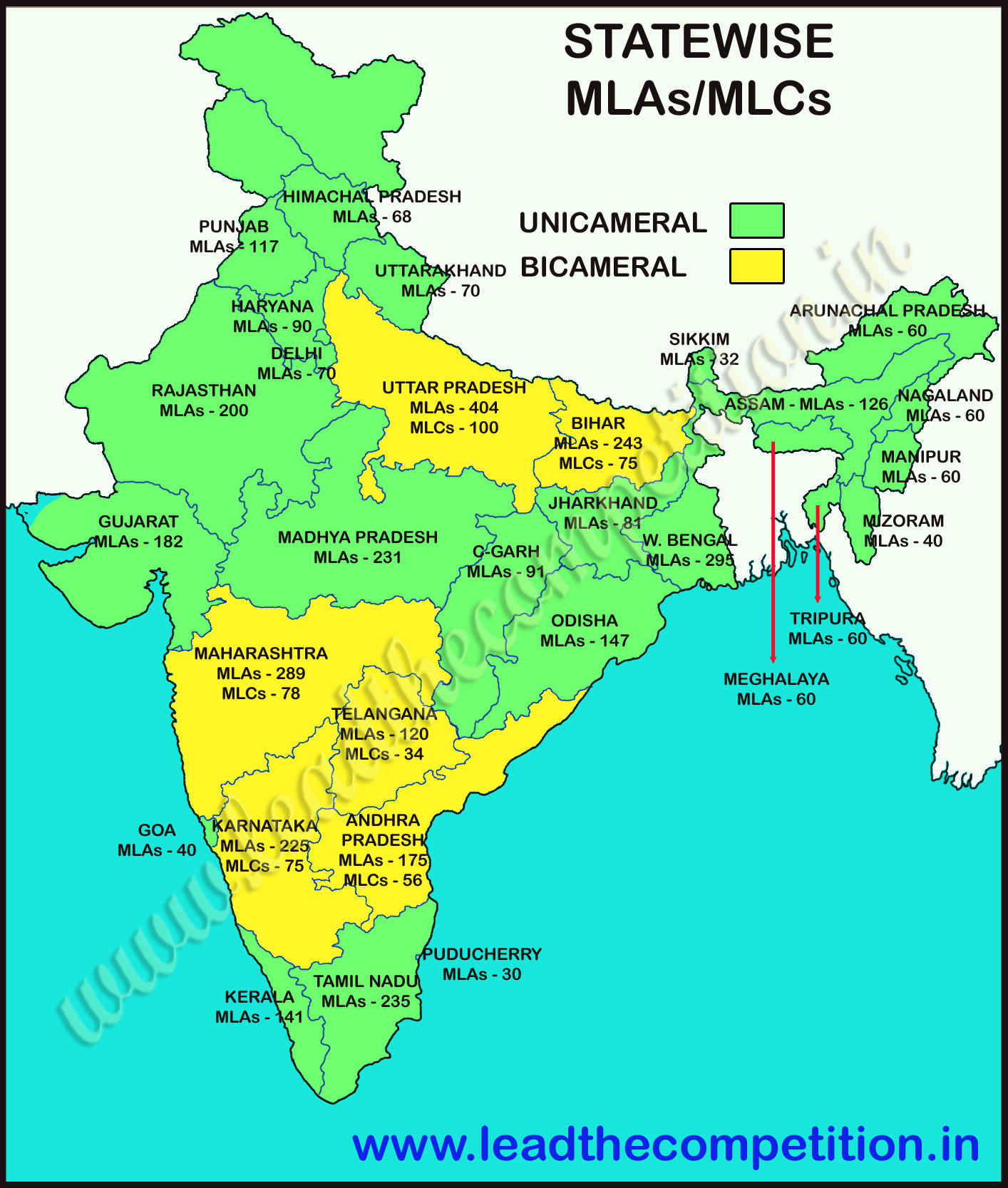
| # | State | LS MPs | RS MPs | MLAs | MLCs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Uttar Pradesh | 80 | 31 | 403 | 100 |
| 2. | Maharashtra | 48 | 19 | 288 | 78 |
| 3. | West Bengal | 42 | 16 | 294 | -- |
| 4. | Bihar | 40 | 16 | 243 | 75 |
| 5. | Tamil Nadu | 39 | 18 | 234 | -- |
| 6. | Madhya Pradesh | 29 | 11 | 230 | -- |
| 7. | Karnataka | 28 | 12 | 224 | 75 |
| 8. | Gujarat | 26 | 11 | 182 | -- |
| 9. | Rajasthan | 25 | 10 | 200 | -- |
| 10. | Andhra Pradesh | 25 | 11 | 175 | 56 |
| 11. | Odisha | 21 | 10 | 147 | -- |
| 12. | Kerala | 20 | 9 | 140 | -- |
| 13. | Telangana | 17 | 7 | 119 | 34 |
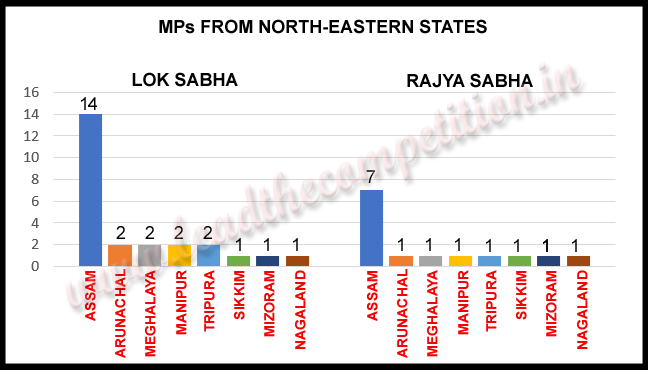
| 14. | Assam | 14 | 7 | 126 | -- |
| 15. | Jharkhand | 14 | 6 | 81 | -- |
| 16. | Punjab | 13 | 7 | 117 | -- |
| 17. | Chhattisgarh | 11 | 5 | 90 | -- |
| 18. | Haryana | 10 | 5 | 90 | -- |
| 19. | Uttarakhand | 5 | 3 | 70 | -- |
| 20. | Himachal Pradesh | 4 | 3 | 68 | -- |
| 21. | Arunachal Pradesh | 2 | 1 | 60 | -- |
| 22. | Goa | 2 | 1 | 40 | -- |
| 23. | Manipur | 2 | 1 | 60 | -- |
| 24. | Meghalaya | 2 | 1 | 60 | -- |
| 25. | Tripura | 2 | 1 | 60 | -- |
| 26. | Mizoram | 1 | 1 | 40 | -- |
| 27. | Nagaland | 1 | 1 | 60 | -- |
| 28. | Sikkim | 1 | 1 | 32 | -- |
| 1. | Delhi | 7 | 3 | 70 | -- |
| 2. | Puducherry | 1 | 1 | 33 | -- |
| 3. | Andaman & Nicobar Is. | 1 | -- | -- | -- |
| 4. | Chandigarh | 1 | -- | -- | -- |
| 5. | Dadra & Nagar Haveli & Daman & Diu | 2 | -- | -- | -- |
| 6. | Lakshadweep | 1 | -- | -- | -- |
| 7. | Jammu & Kashmir | 5 | 4 | 95* | -- |
| 8. | Ladakh | 1 | -- | -- | -- |
| 9. | Nominated | - | 12 | -- | -- |
| Total | 543 | 245 | 4131 | -- | |
| Note: The provision of nominating members of Anglo-Indian community was abolished by the Constitution (104th amendment) Act, 2019 which came into force on 25th January, 2020. In Jammu and Kashmir, the LG may nominate 5 members and in Puducherry, the Centre may nominate 3 members to the Legislative Assembly. | |||||
Statewise MLAs and MLCs List Map
MPs from North Eastern States
Articles Related to MPs, MLAs and MLCs
The following articles of Indian Constitution deal with the number of MPs of Rajya Sabha, Lok Sabha, Members of Legislative Assemblies and Members of Legislative Councils.
Members of Rajya Sabha: Article 80
|
Members of Lok Sabha: Article 81
|
Members of Legislative Assembly of a State: Article 170
|
Members of Legislative Council of a State: Article 171
|
Fourth ScheduleThe distribution of seats of the Rajya Sabha among the States and Union Territories is detailed in the Fourth Schedule to the Constitution of India. |
Acts Related to MPs and MLAs
|
The following Acts of Indian Parliament deal with the allocation of seats among the States and Union Territories of India.
|
The Representation of Peoples Act,1950The legislation was enacted to provide for the allocation of seats in, and the delimitation of constituencies for the purpose of election to, the House of the People and the Legislatures of States, the qualifications of voters at such elections, the preparation of electoral rolls, the manner of filling seats in the Council of States to be filled by representatives of Union territories, and matters connected therewith. |
The Representation of Peoples Act,1951The legislation was enacted to provide for the conduct of elections to the Houses of Parliament and to the House of the Legislature of each State, the qualifications and disqualifications for membership of those Houses, the corrupt practices and other offences at or in connection with such elections and the decision
of doubts and disputes arising out of or in connection with such elections. |
Delimitation ActsA Delimitation Act is passed to provide for the readjustment of the allocation of seats in the House of the People to the States, the total number of seats in the Legislative Assembly of each State, the division of each State and each Union territory having a Legislative Assembly into territorial constituencies for elections to the House of the People and Legislative Assemblies of the States and Union territories. The last Delimitation Act was passed in 2008. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How are the seats of the House of People allocated among the States and UTs?
The seats of the House of People (Lok Sabha) are allocated based on the recommendation of the Delimitation Commission set up under Delimitation Act passed by the Parliament.
What is the most important factor in allocating seats to a particular state?:
The most important factor is the population of the State. The 1971 Census population is used as a base for allocation, due to a constitutional freeze.
As per Article 81(3) of the Constitution the seats should be allocated in such a manner that the ratio of population to seats is roughly equal among states.
What is Delimitation?:
The literal meaning of the word Delimitation is the act of fixing the limits or boundaries of something. So, in context of elections, delimitation refers to drawing or redrawing the boundaries of constituencies.
Why is periodical Delimitation necessary?:
The population growth experienced by any country is generally not uniform and some constituencies may see substantial growth while others may see no or even negative growth. Since democracy essentially aims to be a government of the people, it becomes necessary to ensure proportional representation of people as far as possible.
How many members did the first Lok Sabha have?:
The first Lok Sabha, formed after the first general elections had a total of 489 elected Members of Parliament and 2 nominated members.